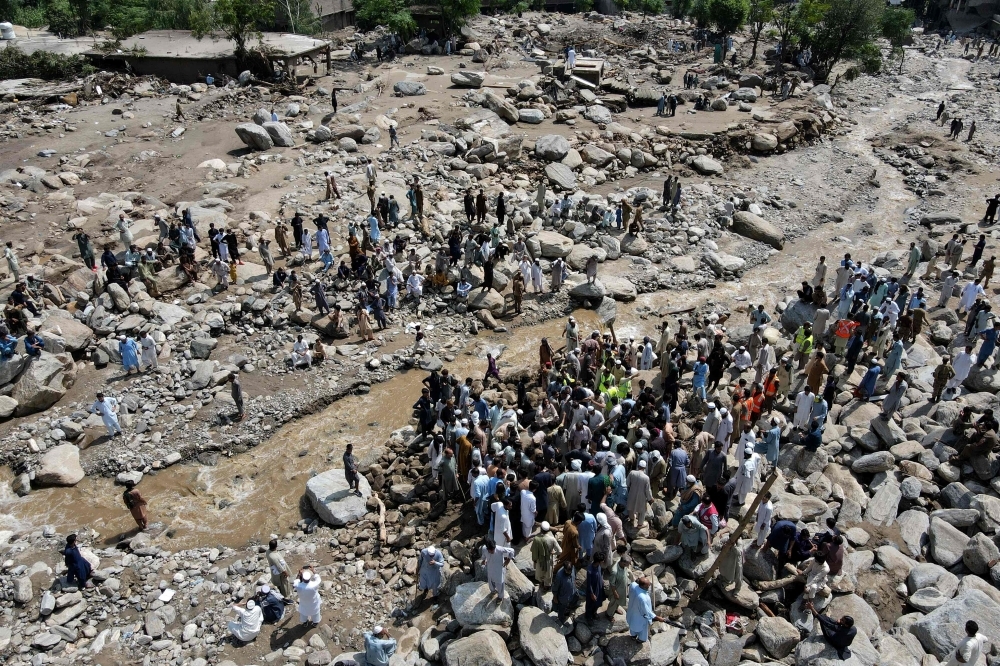
The humanitarian situation across the Gaza Strip remains extremely critical, with severe winter storms threatening to undo recent progress in aid delivery, the United Nations warned on Monday.
Briefing journalists in New York, Stéphane Dujarric, spokesperson for the United Nations Secretary-General, said heavy rains and strong winds are damaging and destroying fragile shelters, leaving tens of thousands of displaced people exposed to cold, mud, and flooding.
“During the past week, our partners delivered supplies to 28,000 families, including 1,600 tents, 16,000 tarpaulins and 27,000 blankets,” he said, stressing that needs remain overwhelming.
More than a million still in urgent need
Despite ongoing relief efforts, at least 1.1 million people—nearly half of Gaza’s population—continue to require urgent humanitarian assistance as weather conditions worsen.
A new storm that struck on Friday once again flooded makeshift camps, destroying tents and leaving thousands without protection. UN teams and humanitarian partners are assessing damage and prioritising the most vulnerable, but they warn that tents are only a temporary solution.
According to the UN, durable shelter solutions are urgently needed, including:
- Construction toolkits and building materials
- Cement and heavy machinery to clear rubble
- Sustained funding to move from emergency aid to early recovery
Infant deaths linked to hypothermia
Children remain among the hardest hit by the crisis.
Health partners report that another infant has died from hypothermia, bringing the total number of reported weather-related infant deaths to four, all of them very young children, according to figures from Gaza’s Ministry of Health.
Since the ceasefire and through the end of 2025, humanitarian partners have:
- Distributed over 310,000 winter clothing kits for children
- Provided 112,000 pairs of shoes
- Installed 150 specialised tents serving as child-friendly and safe spaces
Malnutrition and health concerns
Nutrition teams screened more than 76,000 children last month alone, identifying:
- Around 4,900 cases of acute malnutrition
- Including over 820 cases of severe acute malnutrition
In total, nearly 95,000 cases of acute malnutrition were identified across Gaza during 2025, underscoring the scale of the public-health emergency.
Education under threat
Despite the crisis, education partners continue efforts to protect children’s right to learn.
Last week, 18 new temporary learning spaces opened, supporting about 35,000 students. Gaza now has 440 operational temporary learning spaces, serving approximately 268,000 children.
However, the UN reports that education supplies are still being blocked from entering Gaza by Israeli authorities, who argue that education is not a priority during the first phase of the ceasefire.
“We do believe that it is a critical activity,” Mr. Dujarric said.
A race against time
As winter conditions intensify, UN officials warn that without sustained access, funding, and durable shelter solutions, Gaza’s humanitarian situation could deteriorate even further—especially for children, the displaced, and those already weakened by hunger and illness.

 العربية
العربية








